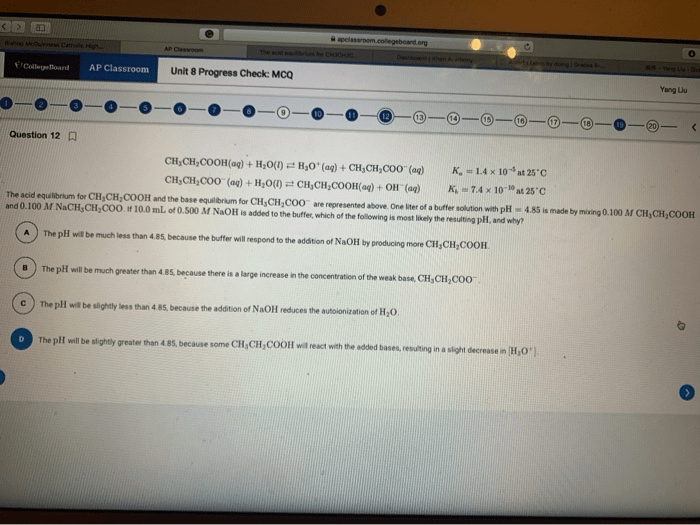
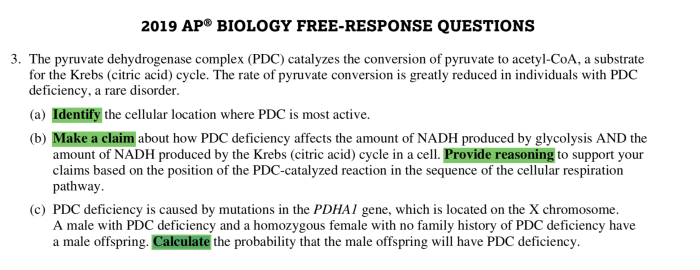
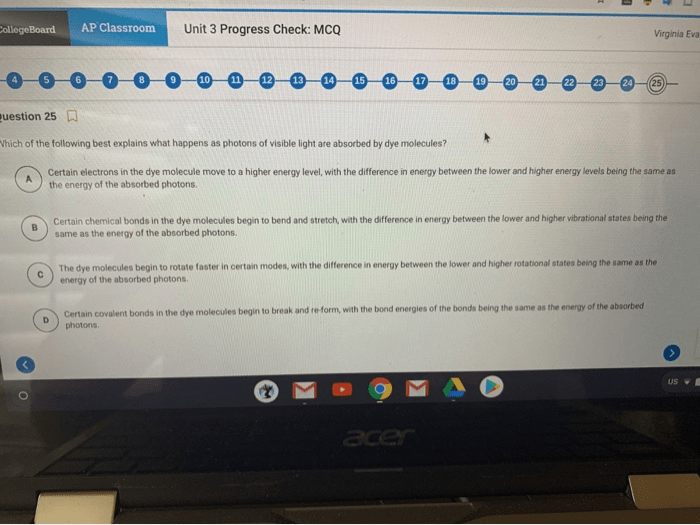
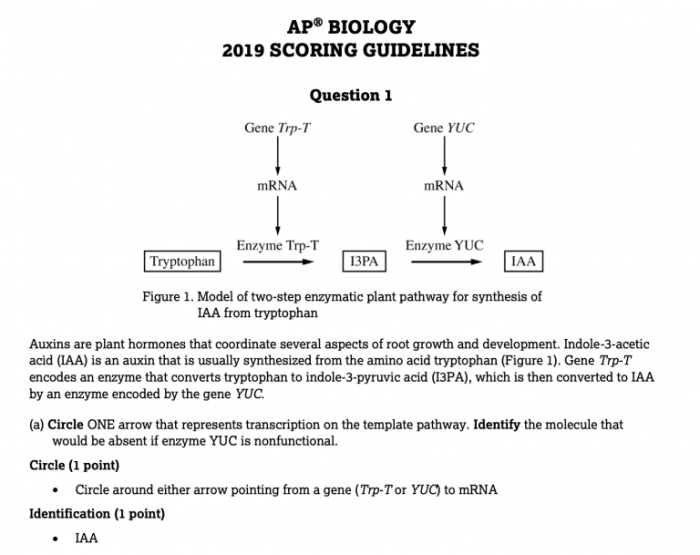
AP Biology Unit 3 Progress Check FRQ is a crucial assessment tool that gauges students’ understanding of fundamental biological concepts. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the FRQ, covering cell communication, cell cycle, Mendelian genetics, molecular genetics, evolution, and ecology.
By delving into the intricacies of these topics, students can enhance their comprehension and prepare effectively for the FRQ.
The FRQ requires students to demonstrate their knowledge and analytical skills through written responses. By understanding the format and expectations of the FRQ, students can develop strategies to approach the questions effectively and showcase their understanding of biological principles.
Cell Communication
Cell signaling is a crucial process that allows cells to communicate with each other and coordinate their activities. There are four main types of cell signaling:
- Paracrine signaling:Involves the release of signaling molecules that act on nearby target cells.
- Endocrine signaling:Involves the release of hormones into the bloodstream, which travel to distant target cells.
- Autocrine signaling:Involves the release of signaling molecules that act on the same cell that produced them.
- Juxtacrine signaling:Involves direct contact between cells, allowing signaling molecules to be transferred directly from one cell to another.
Cell signaling pathways are essential for a wide range of biological processes, including growth, development, differentiation, and immune responses.
Receptors, Ap biology unit 3 progress check frq
Receptors are proteins that bind to signaling molecules and initiate a cellular response. Receptors can be located on the cell surface, in the cytoplasm, or in the nucleus. The specificity of receptors ensures that only the appropriate cells respond to a particular signaling molecule.
Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is the process by which cells grow and divide. It consists of three main stages:
- Interphase:During interphase, the cell grows and prepares for division. It is divided into three sub-stages: G1 (gap 1), S (synthesis), and G2 (gap 2).
- Mitosis:During mitosis, the cell’s chromosomes are divided and separated into two new cells.
- Cytokinesis:During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm is divided into two new cells.
The cell cycle is regulated by a variety of internal and external factors. Dysregulation of the cell cycle can lead to cancer and other diseases.
Mendelian Genetics
Mendelian inheritance is the study of how traits are passed from parents to offspring. According to Mendelian genetics, each trait is controlled by two alleles, one inherited from each parent. The alleles can be dominant or recessive.
- Dominant alleles:Are expressed in the phenotype of the offspring even if only one copy is present.
- Recessive alleles:Are only expressed in the phenotype of the offspring if two copies are present.
Mendelian inheritance patterns can be used to predict the probability of inheriting a particular trait. Exceptions to Mendelian inheritance include incomplete dominance and codominance.
Molecular Genetics: Ap Biology Unit 3 Progress Check Frq
Molecular genetics is the study of the structure and function of DNA and RNA. DNA is the genetic material of cells and contains the instructions for making proteins. RNA is a molecule that is involved in the process of protein synthesis.
- DNA replication:During DNA replication, a new copy of DNA is made.
- Transcription:During transcription, an RNA molecule is made from a DNA template.
- Translation:During translation, a protein is made from an RNA template.
The regulation of gene expression is essential for a wide range of biological processes.
Evolution
Evolution is the process by which the genetic composition of a population changes over time. The theory of evolution by natural selection states that individuals with traits that make them better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
- Evidence for evolution:There is a wide range of evidence for evolution, including fossil records, comparative anatomy, and molecular data.
- Mechanisms of evolution:The main mechanisms of evolution are genetic drift, gene flow, and mutation.
Evolution is an ongoing process that has shaped the diversity of life on Earth.
Ecology
Ecology is the study of the interactions between organisms and their environment.
- Population ecology:Population ecology studies the dynamics of populations, including population growth, carrying capacity, and limiting factors.
- Community ecology:Community ecology studies the interactions between different species within a community.
- Ecosystem ecology:Ecosystem ecology studies the interactions between organisms and their abiotic environment.
Biodiversity is essential for the functioning of ecosystems and provides a wide range of benefits to humans. However, biodiversity is threatened by a variety of human activities.
Questions and Answers
What is the purpose of the AP Biology Unit 3 Progress Check FRQ?
The AP Biology Unit 3 Progress Check FRQ assesses students’ understanding of fundamental biological concepts covered in Unit 3, including cell communication, cell cycle, Mendelian genetics, molecular genetics, evolution, and ecology.
What is the format of the AP Biology Unit 3 Progress Check FRQ?
The AP Biology Unit 3 Progress Check FRQ consists of written response questions that require students to demonstrate their knowledge and analytical skills in biology.
How can I prepare effectively for the AP Biology Unit 3 Progress Check FRQ?
To prepare effectively for the AP Biology Unit 3 Progress Check FRQ, students should thoroughly review the course material, practice answering sample questions, and seek support from teachers or peers if needed.