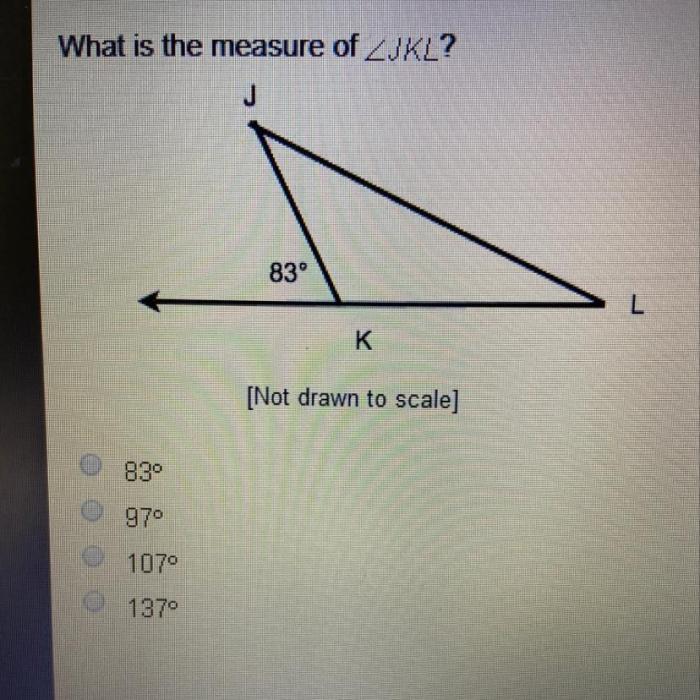
What is the degree measure of jkl – What is the degree measure of angle JKL? This question opens up a fascinating realm of geometry, where we explore the concept of measuring angles and its practical applications. Delving into the properties of angle JKL, we uncover the relationship between radians and degrees, examine adjacent and opposite sides, and unravel the intricacies of complementary and supplementary angles.
Our journey culminates in exploring real-world scenarios where the degree measure of angle JKL plays a pivotal role, empowering us to solve practical problems and navigate the world around us.
As we embark on this exploration, we will encounter special cases of angle JKL, such as right angles, acute angles, and obtuse angles, each possessing unique characteristics and properties. Through examples and illustrations, we will gain a deeper understanding of these different types of angles and their significance.
Degree Measure of Angle JKL: What Is The Degree Measure Of Jkl
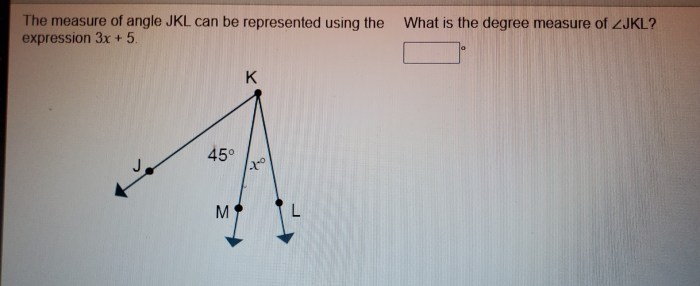
The degree measure of an angle is a measure of the angle’s size. It is expressed in degrees, which are units of angular measurement. The degree measure of an angle is calculated by dividing the measure of the angle in radians by 2π.
The formula for calculating the degree measure of angle JKL is:
degree measure of angle JKL = (measure of angle JKL in radians) / 2π
For example, if the measure of angle JKL in radians is 1.57 radians, then the degree measure of angle JKL is 90 degrees.
Geometric Properties of Angle JKL, What is the degree measure of jkl
The adjacent sides of angle JKL are the two sides that form the angle. The opposite side of angle JKL is the side that is opposite the vertex of the angle.
Complementary angles are two angles that add up to 90 degrees. Supplementary angles are two angles that add up to 180 degrees.
The angles formed by intersecting lines are either complementary or supplementary.
Applications of Angle JKL
The degree measure of angle JKL is relevant in many real-world applications, such as:
- Architecture
- Engineering
- Navigation
In architecture, the degree measure of angles is used to determine the slope of roofs and the angle of walls.
In engineering, the degree measure of angles is used to determine the angle of bridges and the angle of airplane wings.
In navigation, the degree measure of angles is used to determine the direction of travel.
Special Cases of Angle JKL
There are several special cases of angle JKL, including:
- Right angles
- Acute angles
- Obtuse angles
Right angles are angles that measure 90 degrees. Acute angles are angles that measure less than 90 degrees. Obtuse angles are angles that measure greater than 90 degrees.
Questions and Answers
What is the formula for calculating the degree measure of angle JKL?
The degree measure of angle JKL can be calculated using the formula: m∠JKL = (180/π) × θ, where θ is the measure of the angle in radians.
What is the relationship between radians and degrees?
Radians and degrees are two different units for measuring angles. One radian is equal to approximately 57.3 degrees, and one degree is equal to approximately 0.01745 radians.
What are the properties of angles formed by intersecting lines?
When two lines intersect, they form four angles. These angles are called vertical angles (opposite angles) and adjacent angles (angles that share a side). Vertical angles are congruent, and adjacent angles are supplementary.